HazMat Coveralls & Suits
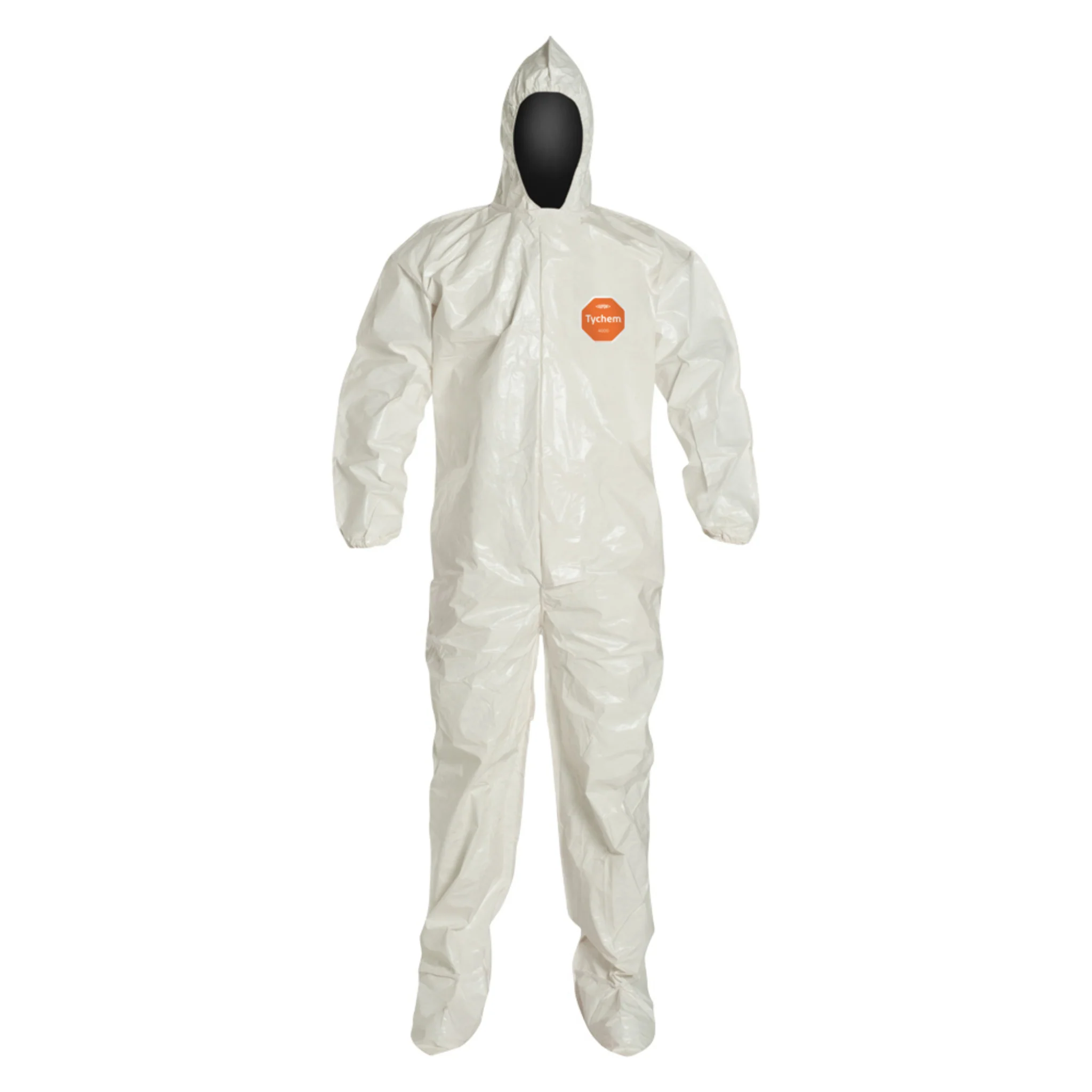
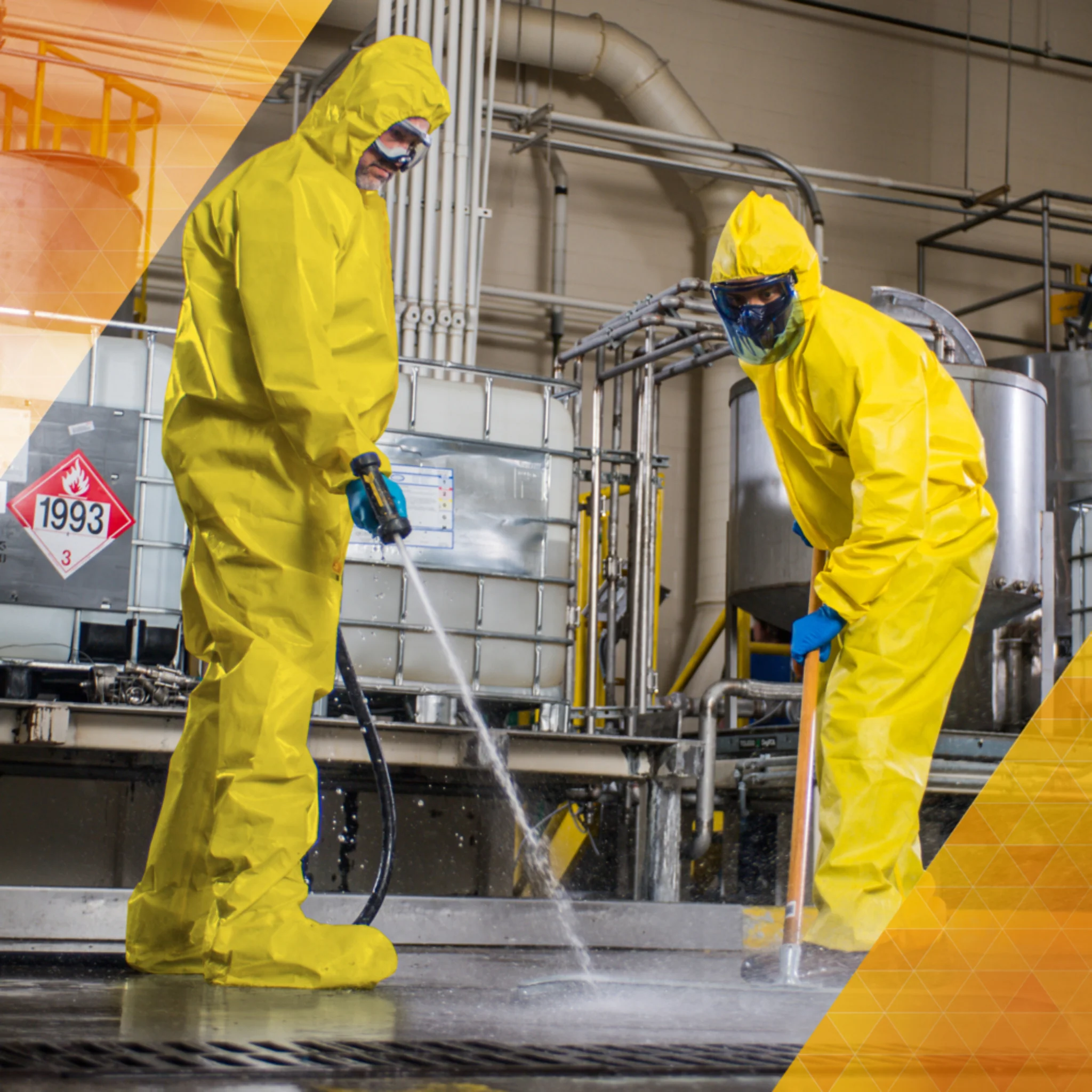
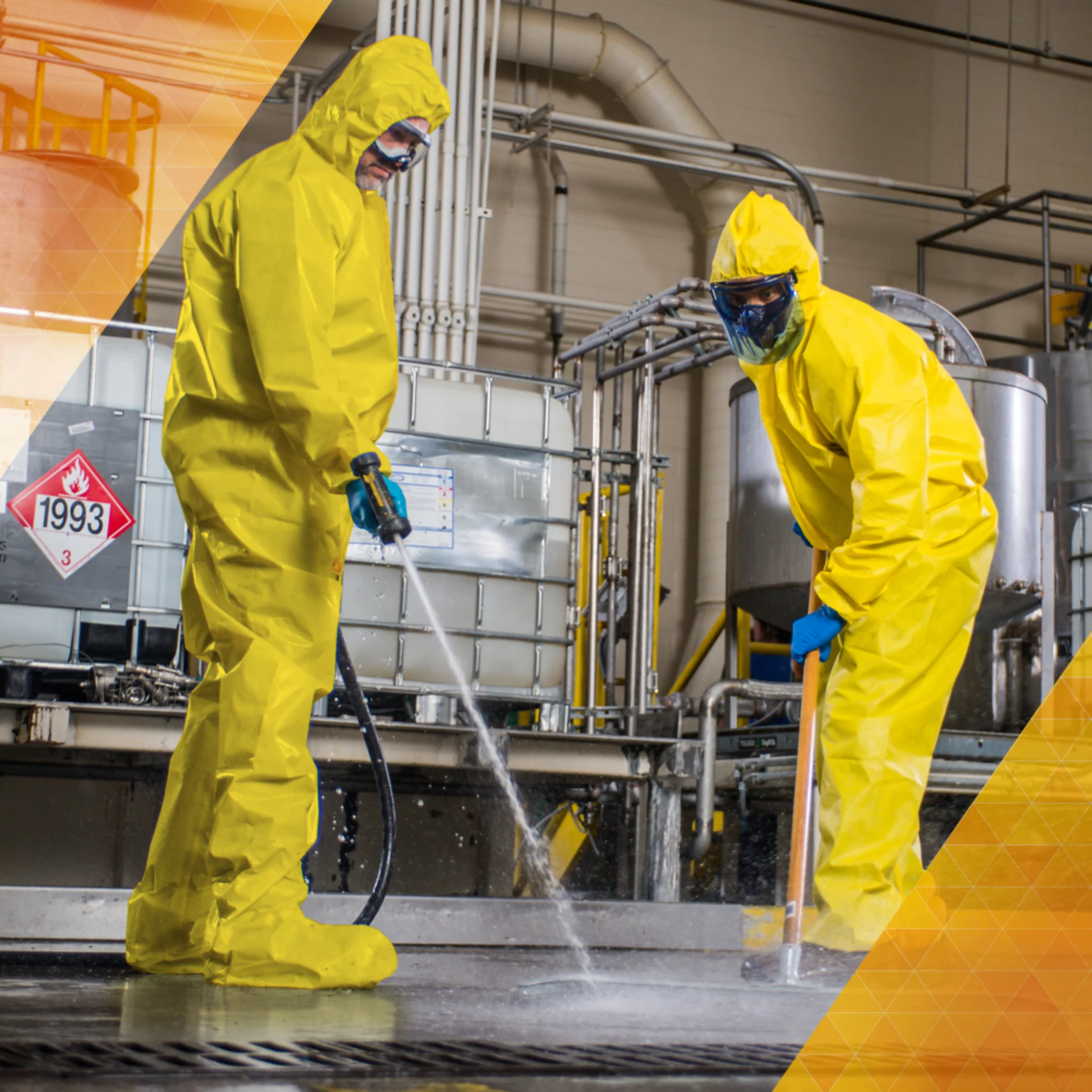















































Enviro Safety is a leading distributor in Hazmat suit and disposable coveralls and protective clothing, offering a variety of options that apply to many situations. Protect yourself from harmful materials by using Enviro Safety Products’ extensive line of hazmat suits, from Class A models to disposable coveralls and chemical-resistant varieties. Our safety specialists are on standby to answer any questions you may have about which suit is right for you. We sell the most popular lines, including DuPont™ and Lakeland. We understand all the risks that come with a hazardous work situation and want you to feel safe and protected. You can click below to learn about the difference in Coveralls as well as click into our top selling brands to purchase MicroMax Coveralls and Tyvek® coveralls. We also specialize in Dupont™ Proshield and several other specialized lines.
Comprehensive Coverage is Easy with HazMat Suits from Enviro
When working in an industry where there is a strong need for hazmat protective clothing, whether it’s Class A coveralls or chemical-resistant disposable gear, safety is the main priority. Our clothing is created to provide protection from hazmat materials and substances. The high quality of our suits and coveralls ensures a high performance level while retaining low, affordable prices. We keep our clothing accessible as we understand the need for safety. For the highest level of shielding, try a Class A hazmat suit. When more moderate coverage is needed, our line of disposable coveralls from ChemMax, Tychem® and Tyvek® are a great fit. Find the protective clothing that suits your work environment with our selection of chemical-resistant hazmat suits from Enviro Safety Products.
Our protective clothing provides the best in quality and care and is the key to keeping yourself protected against hazardous elements. This wide-range of products includes items that are disposable as well as durable. We offer a collection of Class A hazmat suits that comply with federal regulations and guard against disease with top-quality materials. Suit up and seal out chemicals and other harmful substances with our array of disposable protective clothing that meets Class A standards.
Seam Types
Serged Seam
A serged seam joins two pieces of material with a thread stitch that interlocks. This is an economical stitching method for general applications. Chemical protective clothing generally does not employ this stitching method. It is more commonly found on limited use clothing where dry particulates are of a concern.Sewn and Bound Seam
This seam joins two pieces of material with an overlay of similar material and is chain stitched through all of the layers for a clean, finished edge. This provides increased holdout of liquids and dry particulates.Heat Sealed Seam
A heat-sealed seam is sewn and then sealed with heat-activated tape. This method provides liquid-proof seams and is especially useful for Level A and B chemical protective clothing.Heat Sealed Plus Seam
This is the strongest seam offered. This seam is created by sewing and then heat-sealing the outside and inside to offer the highest strength and chemical resistance.Protecting Against Measles Outbreak
U.S. Measles Outbreaks Hit Highest Level in More Than 25 Years. The CDC says 971 cases have been reported in the United States for 2019 as of May 30th 2019. With the outbreak of measles throughout the United States, it is more important than ever to be prepared. In addition to vaccination, First responders, as well as others can suit up in PPE to reduce person-to-person transmission of the virus between people, in the event of a measles outbreak.
Homeless Encampment Clean Out
Stay safe during homeless encampment clean outs. When cleaning out a homeless encampment, clean up crews and first responders are going to encounter a multitude of hazards. From Hypodermic needles and syringes to human waste and garbage, the most important thing a person can do is outfit themselves in proper PPE to protect themselves and their team. Homeless encampments continue to be a breeding ground for diseases such as Typhus and Hepatitis. Due to the amount of drug use, “poor sanitary conditions” including leftover and rotted food, human waste and hypodermic needles, first responders and cleanup crews need to be prepared. Blood-Borne pathogens are another risk during homeless encampment cleanup.
Ebola Safety and PPE
Ebola has continued to be a problem throughout Africa. Over the years we have continued to see outbreaks on the African continent. In the healthcare settings, the Ebola virus is spread through direct contact with blood or body fluids of a person who is sick with Ebola or with communal objects (e.g., bathroom surfaces, medical equipment) that have been contaminated with infectious blood or body fluids. The Ebola virus in blood and body fluids can enter a person’s body through broken skin or unprotected mucous membranes in, for example, the eyes, nose, or mouth. It is very important for all healthcare workers caring for patients with Ebola, PPE that fully covers skin and clothing and prevents any exposure of the eyes, nose, and mouth, as well as open wounds, such as cuts on hands, it is recommended to reduce the risk of accidental self-contamination of mucous membranes or broken skin. All proper PPE must be used in the context of a comprehensive infection control program that follows CDC recommendations and applicable Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSHA) requirements, including the Bloodborne Pathogens (29 CFR 1910.1030)external icon, PPE (29 CFR 1910.132)external icon, and Respiratory Protection (20 CFR 1910.134)external icon standards, and other requirements under OSHA (e.g., the General Duty Clause, section 5(a)(1); and prohibitions against discrimination or retaliation against workers, section 11(c)). Ebola can be fatal and it is highly recommended if you think you have been exposed to the Ebola virus to receive immediate medical attention. To protect healthcare workers who are caring for patients with Ebola, healthcare facilities must provide onsite management and oversight of adherence to safely using PPE, and implement administrative and environmental controls with continuous safety checks through direct observation of healthcare workers, including during the PPE donning and doffing steps.
NFPA Standards
NFPA1991: Standard on Vapor-Protective Ensembles for Hazardous Materials Emergencies and CBRN Terrorism Incidents (2016 Edition) This is one of the highest safety standards on the books, calling for fully encapsulated chemical protection covering 100% of the wearer’s body. A self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) is absolutely necessary when using protection of this caliber. The chemical barrier must be broad, emcompassing liquids and gases, toxic industrial chemicals (TICs) and chemical warfare agents (CWAs). The protection must be gas-tight and hold up under pressure, with limited flame resistance. The standard is consistent with EPA/OSHA Level A.
NFPA1992: “Standard on Liquid Splash-Protective Ensembles and Clothing for Hazardous Materials Emergencies” (2018 Edition) This is the standard for protective coverall garments that feature penetration barriers against liquids (not vapors). The garment can be one- or multi-piece, as long as it passes the relevant tests. Garments can be certified by themselves or as an ensemble (with specific respirators or other accessories). The standard is consistent with EPA/OSHA Level B.
NFPA1994: “Standard on Protective Ensembles for First Responders to Hazardous Materials Emergencies and CBRN Terrorism Incidents” (2018 Edition) This is standard is divided into four “classes” of protective ensembles: Class 1 ensembles protect emergency first responders in situations that involve vapor or liquid chemical hazards in concentrations that are considered immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH). Self-contained breathing apparati (SCBA) are required in these environments.
Class 2 ensembles provide limited protection to first responders in situations where vapor or liquid chemical hazards are at or above IDLH levels. These situations require SCBA equipment as well.
Class 3 ensembles provide limited protection to first responders when hazard levels are below IDLH levels, allowing for the use of air-purifying respirators that aren’t necessarily self-contained.
Class 4 ensembles provide limited protection to first responders in situations with particulate hazards at concentrations below IDLH. Biological and radiological particulate should be protected from in this class, and air-purifying respirators are usable as well.
NFPA2112: “Standard on Flame-Resistant Clothing for Protection of Industrial Personnel Against Short-Duration Thermal Exposures from Fire” (2018 Edition) This standard dictates the minimum performance requirements for flame-resistant garments. Garments are subjected to tests that gauge their thermal insulation, heat stability, flame engulfment resistance, and the stability of the components (threads, zippers, etc.). To be compliant, garments must achieve a 50% or less predicted body burn, extinguish flames on their surfaces quickly and resist melting, and be appropriately and clearly labeled.
ASTM International (ASTM) Standards
ASTM F903 - 18 "Standard Test Method for Resistance of Materials Used in Protective Clothing to Penetration by Liquids"
This test method is used to test specimens of protective clothing and candidate materials and constructions to be used in protective clothing. The resistance to visible penetration of the test liquid is determined with the liquid in continuous contact with the normally outside surface of the test specimen.
ASTM F739 - 12e1 "Standard Test Method for Permeation of Liquids and Gases through Protective Clothing Materials under Conditions of Continuous Contact"
This test method measures the permeation of liquids and gases through protective clothing materials under the condition of continuous contact.
ASTM F1671 / F1671M - 13 "Standard Test Method for Resistance of Materials Used in Protective Clothing to Penetration by Blood-Borne Pathogens Using Phi-X174 Bacteriophage Penetration as a Test System "
This test method is used to measure the resistance of materials used in protective clothing to penetration by blood-borne pathogens using a surrogate microbe under conditions of continuous liquid contact. Protective clothing material pass/fail determinations are based on the detection of viral penetration.
ASTM F2815 - 10(2014) "Standard Practice for Chemical Permeation through Protective Clothing Materials: Testing Data Analysis by Use of a Computer Program"
This practice covers the calculations of all the permeation parameters related to Test Method F739, ISO 6529, and Practice D6978 standards by use of a computer program, referred to as “Permeation Calculator” (DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2007?–?143c).
ASTM F1407 - 12(2017) "Test method for resistance of chemical protective clothing materials to liquid permeation - permeation cup method"
This test Method A definitive procedure that produces a test result: Examples of test methods include, but are not limited to: identification, measurement, and evaluation of one or more qualities, characteristics, or properties. A precision and bias statement shall be reported at the end of a test method.
ASTM F1383 - 12e1 "Standard Test Method for Permeation of Liquids and Gases through Protective Clothing Materials under Conditions of Intermittent Contact"
This test Method A definitive procedure that produces a test result: Examples of test methods include, but are not limited to: identification, measurement, and evaluation of one or more qualities, characteristics, or properties. A precision and bias statement shall be reported at the end of a test method.
ASTM F1494 - 14 "Standard Terminology Relating to Protective Clothing"
This standard defines the specialized terms used in standards developed by Committee F23 on Protective Clothing.
ASTM F1001 - 12(2017) "Standard Guide for Selection of Chemicals to Evaluate Protective Clothing Materials"
This guide establishes a recommended list of challenge chemicals to encourage those who evaluate chemical protective clothing to test a minimum number of chemicals in common. This list will simplify the comparison of data from different sources. This guide may also serve material developers or evaluators in screening candidate protective clothing materials.
ASTM F1194 - 18 "Standard Guide for Documenting the Results of Chemical Permeation Testing of Materials Used in Protective Clothing"
This guide provides a format for documenting information and performance data to encourage thorough and consistent documentation from a permeation test. Uniform information and performance data increase the likelihood of selecting proper chemical protective clothing material (CPC) by permitting direct comparisons of one product with another.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standards
29 CFR 1910.1030 "Bloodborne pathogens"
This standard shall specify the minimum responsibilities of an employer to provide PPE such as, but not limited to, gloves, gowns, laboratory coats, face shields or masks and eye protection, and mouthpieces, resuscitation bags, pocket masks, or other ventilation devices when an employee is potential exposed to bloodborne pathogens. Please note that there are 28 OSHA-approved occupational safety and health State Plans. State Plans are required to have standards and enforcement programs that are at least as effective as federal OSHA’s and may have different or more stringent standards related to PPE. More information about State Plans and their standards is available at: https://www.osha.gov/dcsp/osp/index.html
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
ISO 6529:2013 "Protective clothing -- Protection against chemicals -- Determination of resistance of protective clothing materials to permeation by liquids and gases"
ISO 6529:2013 describes laboratory test methods to determine the resistance of materials used in protective clothing, including gloves and including footwear, when the footwear is an integral part of the clothing, to permeation by liquid or gaseous chemicals under the conditions of either continuous or intermittent contact. Method A is applicable to testing against liquid chemicals, either volatile or soluble in water, expected to be in continuous contact with the protective clothing material. Method B is applicable to testing against gaseous chemicals expected to be in continuous contact with the protective clothing material. Method C is applicable to testing against gaseous and liquid chemicals, either volatile or soluble in water, expected to be in intermittent contact with the protective clothing material. These test methods assess the permeation resistance of the protective clothing material under laboratory conditions in terms of breakthrough time, permeation rate and cumulative permeation. These test methods also enable qualitative observations to be made of the effects of the test chemical on the material under test. These test methods are only suitable for measuring permeation by liquids and gases. These test methods address only the performance of materials or certain materials' constructions (e.g. seams).
From white hazmat suits, considered disposable coveralls, to full hazmat bio hazard suits offering protection from liquid or gaseous form, Enviro Safety offers the hazmat suits for sale you need at the protection levels you require. Military personnel should stay protected from biological agents using the correct chemical suits as applicable.
Embracing the Shield: The Hazmat Suit and Proper Protection in Hazardous Environments
In today's world, where safety is paramount, the hazmat suit reigns as the epitome of real protection. Designed to shield individuals from hazardous substances and dangerous environments, this chem suit, with its formidable splash protection capabilities, stands as a symbol of safety. Whether it's dealing with radioactive materials or toxic chemicals, wearing this personal protective equipment ensures the utmost defense for the wearer. From head to toe, every inch is covered, leaving no room for compromise. The respiratory system, an invaluable asset, finds solace within the suit's integrated mask and filter, providing a secure barrier against harmful particles. When it comes to confronting hazardous elements, nothing beats the importance of proper protection, and the hazmat suit offers precisely that— an unyielding fortress that enables individuals to navigate the treacherous realms with confidence.
Safeguarding with Unbeatable Assurance: Hazmat Suit Price and Enhanced Full Body Protection
In an era where safety takes precedence, the significance of protective gear cannot be overstated. The realm of hazmat suits, HVAC suits, and disposable apparel has evolved to offer comprehensive safeguarding solutions, ensuring enhanced personal protection. The hazmat suit price is not merely an investment but a reflection of the invaluable reassurance it provides. These meticulously designed suits incorporate a full body shield, fortified with high-quality materials, creating an impenetrable barrier against hazardous substances. With an attached hood as a vital component, these suits offer an additional layer of safeguarding, leaving no room for compromise. In a world where safety is paramount, these suits provide added protection that goes beyond measure, empowering individuals to face daunting challenges with unwavering confidence.
What is a hazmat suite?
A Hazmat suit is a type of protective clothing which cover the entire body, including the head, torso, arms, and legs worn by individuals who are dealing with or working in environments that contain hazardous materials or substances. It is designed to protect the wearer from exposure to dangerous chemicals, toxins, or infectious agents.
Decontamination suits applications:
- Chemical spills and cleanups
- Biological or viral outbreaks
- Nuclear emergencies
- Hazardous material handling and transportation
- Industrial accidents
- Medical research and biohazard containment
- Emergency response teams, such as firefighters and first responders
Hazmat Suit
A hazmat suit, also known as a quarantine suit, is a type of personal protective equipment (PPE) that protects the wearer from hazardous substances, such as chemicals, biological agents, or radioactive materials. Hazmat suits are designed to prevent the contamination of the skin, eyes, respiratory system, and clothing of the wearer.
Types of Hazmat Suits
There are different types of hazmat suits, depending on the level of protection required and the nature of the hazard. Some common types are:
- Level A: This is the highest level of protection, which covers the entire body and includes a self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) or a supplied-air respirator (SAR). Level A suits are used when there is a high risk of exposure to unknown or extremely toxic substances, or when there is a lack of oxygen in the environment.
- Level B: This is similar to Level A, but without the SCBA or SAR. Level B suits are used when there is a moderate risk of exposure to substances that can cause serious health effects, but the respiratory system is not at risk.
- Level C: This is a lower level of protection, which covers most of the body and includes an air-purifying respirator (APR) or a powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR). Level C suits are used when there is a low risk of exposure to substances that can cause minor health effects, and the type and concentration of the substance are known.
- Level D: This is the lowest level of protection, which consists of normal work clothes and basic PPE, such as gloves, goggles, and boots. Level D suits are used when there is no risk of exposure to hazardous substances, but there is a need to protect against general dirt and debris.
Green Hazmat Suit
A green hazmat suit is a type of Level C suit that is commonly used by medical personnel, emergency responders, and decontamination workers. A green hazmat suit is made of a durable and breathable material that can resist tears and punctures. A green hazmat suit also has an attached hood and boots, elastic cuffs and ankles, and a zipper closure. A green hazmat suit can protect the wearer from splashes and sprays of liquids or aerosols that may contain infectious agents or toxins.
Hazmat Suit with Respirator
A hazmat suit with respirator is a type of Level C suit that has an additional feature of a respirator device that filters the air that the wearer breathes. A hazmat suit with respirator can be either an APR or a PAPR, depending on the availability and preference of the wearer. An APR is a mask-like device that fits over the nose and mouth and has cartridges that filter out specific contaminants from the air. A PAPR is a battery-powered device that has a blower that draws air through a filter and delivers it to a hood or mask that covers the head and face. A hazmat suit with respirator can protect the wearer from inhaling harmful particles or vapors that may be present in the environment.
Cheap Hazmat Suit
A cheap hazmat suit is a type of Level D suit that is made of low-quality or disposable material that can provide minimal protection from dirt and debris. A cheap hazmat suit may not have any special features or accessories, such as hoods, boots, cuffs, or zippers. A cheap hazmat suit may also have poor fit, durability, or comfort. A cheap hazmat suit is not recommended for use in situations where there is any risk of exposure to hazardous substances, as it may not provide adequate protection for the wearer.
Air Flow and Suit Material
Air flow and suit material are two important factors that affect the performance and comfort of a hazmat suit. Air flow refers to the amount and direction of air that circulates inside and outside the suit. Air flow can affect the temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels inside the suit, as well as the removal of contaminants from the suit. Suit material refers to the type and quality of fabric that is used to make the suit. Suit material can affect the resistance, breathability, flexibility, and weight of the suit.
A good hazmat suit should have sufficient air flow to prevent heat stress, dehydration, or suffocation for the wearer. A good hazmat suit should also have suitable suit material to prevent penetration, permeation, or degradation by hazardous substances. A good hazmat suit should also be comfortable and easy to wear for long periods of time.
The Hazmat Suit - Your Shield Against Hazardous Environments
When it comes to safeguarding yourself in potentially perilous situations, few garments are as iconic and essential as the hazmat suit. Whether you're facing chemical spills, biological threats, or radioactive materials, this protective gear has your back—literally.
In this article, we'll dive into the world of hazmat suits, including the versatile blue hazmat suit, the costs involved, and its close cousin, the isolation suit.
The Versatile Blue Hazmat Suit: Function Meets Style
While the primary focus of a hazmat suit is safety, there's no harm in looking good while you're at it. Enter the blue hazmat suit—a modern twist on a classic necessity. The blue hue not only adds a touch of style but also serves a practical purpose. It helps identify wearers more easily, which can be crucial in emergency situations. But what else sets it apart from its traditional yellow counterpart?
Breaking Down Hazmat Suit Costs: Protecting Yourself on a Budget
One common concern when considering a hazmat suit is the cost. Is it possible to find quality protection without breaking the bank? The answer is yes, but it depends on your specific needs. Hazmat suit cost can vary widely based on factors like material, level of protection, and brand. We'll help you navigate the price spectrum and make an informed choice. Isolation Suits: When Precision Matters
Isolation suits are closely related to hazmat suits but serve a slightly different purpose. While hazmat suits are designed to protect against a wide range of hazards, isolation suits are often used in healthcare settings to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. These suits are crucial in maintaining a sterile environment in hospitals and laboratories.
Hazmat Jackets: A Modular Approach to Safety
Hazmat jackets, sometimes called hazmat jackets with hoods, offer a more modular approach to personal protection. These jackets can be worn over existing clothing and are especially useful when full-body protection isn't necessary. They are commonly used in scenarios where chemical splashes or exposure to hazardous materials are potential risks.
Conclusion - Your Safety, Your Choice
In conclusion, whether you opt for a traditional hazmat suit, a stylish blue hazmat suit, or a more specialized isolation suit, the key is to prioritize safety. Understanding the hazmat suit cost and its variations is essential to make the right choice for your unique needs. Additionally, don't forget about the versatile hazmat jackets, which provide a more flexible approach to protection. When it comes to safeguarding yourself in hazardous environments, the right gear can make all the difference.
Ensuring Safety in Hazardous Work Environments
If you work in laboratories, factories, farms, hospitals, or even in nature, it can be dangerous, so you need to wear the right protective gear. A hazmat suit is a kind of clothing that covers your whole body and shields you from harmful substances. It helps you do your job safely and avoid touching or breathing in anything that could harm you. If you run a business that involves chemicals or biological agents, you must ensure your employees’ safety, which can prevent serious issues for your company. Exposure to chemicals or biological agents can lead to severe health problems, such as skin rashes, breathing difficulties, infections, or even death.
How to Find and Buy a Hazmat Suit and a Guide for Safety Seekers
You can find a list of such stores by searching for "hazmat suit near me" or "hazmat suits near me" on your web browser. You can also use the "related searches" feature to find more specific results, such as "hazmat suit for sale". However, before you visit a store, make sure you have the proper access and permission to buy a hazmat suit. Some stores may require you to show proof of your occupation, training, or certification to ensure that you are qualified to use a hazmat suit.
Another option is to order a hazmat suit online from a reputable vendor. You can find many websites that sell hazmat suits by searching for "where to get a hazmat suit" or "hazmat suit nearby" on your web browser. You can also compare prices, features and reviews of different hazmat suits by using the "related searches" feature. However, before you order a hazmat suit online, make sure you check the delivery time and shipping costs. Some websites may take longer to deliver or charge extra fees for shipping hazmat suits. You should also verify that the website is secure and trustworthy by checking the http protocol and the server information.




